Difference between revisions of "IoT - ESP-Everything!"
(→I/O) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
*Actual mounting holes! | *Actual mounting holes! | ||
| − | === The Building Blocks === | + | ===The Building Blocks=== |
| − | ==== Power ==== | + | ====Power==== |
| + | [[File:ESP-Everything Power 3d.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| − | * Input: | + | *Input: |
| − | ** Directly soldered USB-micro connector (J1) | + | **Directly soldered USB-micro connector (J1) |
| − | ** My favourite USB breakout board (J2) | + | **My favourite USB breakout board (J2) |
| − | ** Direct wiring (J2) | + | **Direct wiring (J2) |
| − | * Reverse polarity protection (D1) | + | *Reverse polarity protection (D1) |
| − | * Regulation (U1 & C1) | + | *Regulation (U1 & C1) |
| − | * Indication (R2D2) :P | + | *Indication (R2D2) :P |
| − | ==== Programming ==== | + | ====Programming==== |
| + | [[File:ESP-Everything Programming 3d.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| − | * Header (J3) | + | *Header (J3) |
| − | ** Pins 1-4 are an exact match for the most common layout used on Sonoff devices. | + | **Pins 1-4 are an exact match for the most common layout used on Sonoff devices. |
| − | ** Pins 5 & 6 are used (with an appropriate USB-Serial adapter to enable the automatic mode selection | + | **Pins 5 & 6 are used (with an appropriate USB-Serial adapter to enable the automatic mode selection |
| − | ** RST is actually atest point & should be just another pin on J3. But, I didn't originally plan to put it directly inline with J3... so... | + | **RST is actually atest point & should be just another pin on J3. But, I didn't originally plan to put it directly inline with J3... so... |
| − | * Automatic mode selection (Q1 & Q2) | + | *Automatic mode selection (Q1 & Q2) |
| − | ** This idea was shamelessly stolen from the D1-mini | + | **This idea was shamelessly stolen from the D1-mini |
| − | ==== I/O ==== | + | ====I/O==== |
| + | [[File:ESP-Everything IO 3d.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| − | * GPIO breakout (J6) | + | *GPIO breakout (J6) |
| − | ** The ESP8266 (& ESP8285) have 17 GPIO & 1 ADC available. Therefore, I've placed an 18 pin header for I/O on the board. | + | **The ESP8266 (& ESP8285) have 17 GPIO & 1 ADC available. Therefore, I've placed an 18 pin header for I/O on the board. |
| − | * Power for sensors etc. (J5) | + | *Power for sensors etc. (J5) |
| − | ** Obvious once you look at the board... 18 pins... | + | **Obvious once you look at the board... 18 pins... |
| − | * Ground for sensors etc. (J4) | + | *Ground for sensors etc. (J4) |
| − | ** Obvious once you look at the board... 18 pins... | + | **Obvious once you look at the board... 18 pins... |
You will notice that ALL of the boards have the full set of I/O pins. On some (most) of the boards, you'll see (at least on the board views & renders) that some of the GPIO, 3v3 & GND sets are crossed out. The GPIOs are not all broken out on all modules. But, I've left the pin positions in to keep all the boards compatible with each other. | You will notice that ALL of the boards have the full set of I/O pins. On some (most) of the boards, you'll see (at least on the board views & renders) that some of the GPIO, 3v3 & GND sets are crossed out. The GPIOs are not all broken out on all modules. But, I've left the pin positions in to keep all the boards compatible with each other. | ||
| − | ==== The Module Carrier ==== | + | ====The Module Carrier==== |
| + | [[File:ESP-Everything Module 3d.png|none|thumb]] | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| − | * All the empty space on the board... :P | + | *All the empty space on the board... :P |
===The Resulting Set of Boards=== | ===The Resulting Set of Boards=== | ||
Revision as of 20:42, 14 October 2020
My personal response to the weirdness that is ESP module form factors.
My introduction to ESP was the ESP-07.
It's an awesome module to play with. But it has a few issues.
Contents
The Issues
Issue #1: ESP devices run on 3.3V, not the ubiquitous 5V you can easily get by grabbing the nearest spare phone charger. This one's pretty simple. Put a 3.3V regulator in there. (I tend to grab the AMS1117-3.3. Cheap & easy...)
Issue #2: Every standard ESP module has a weird pinout at a weird pin pitch. Dunno why. They just do. Even the ESP-01 has a pain-in-the-ass pin layout. (but, at least it's on 0.1" spacing. Too bad it's designed to avoid breadboard compatibility...)
Issue #3: The most annoying one... To program an ESP chip, you have to hold gpio0 low during bootup or reset. Then you have to reset the board again to get out of programming mode. I get why they did it this way, but it's annoying.
Some available solutions
There are a number of cheap modules available that are basically either carriers for ESP modules or extensions of the ESP modules..
The LOLIN D1 mini is a favourite... It's "breadboard friendly" (as long as you don't mind it using up most of the width.) It has on-board regulation to run off 5V. It also has an onboard USB to Serial chip AND solves the gpio0 issue.
Sadly, most of these are in form factors that are not conducive to embedding in a finished project.
Also... I have an aversion to permanently installing a UART chip in devices that, once finished, will likely never need them again. When I'm working on a microcontroller project, I have a selection of UART modules handy to simply connect for programming. Afterwards, it's a redundant item.
So...
What I've done to try & solve a few of these issues
After discovering the ESP-M3, I determined that it would be nearly ideal for embedding into projects.
So I set out to design a carrier board for it.
& the whole bloody project got a little out of hand.
Basic Design requirements
- Power via random phone charger (or any other 5V source really)
- Make it hard to blow up with reverse power
- Programming header
- Compatible with the typical Sonoff header would be good
- Capable of automatic mode selection
- Breakout ALL available gpio pins from the module
- Putting them in some sort of logical order would be awesome
- Include 3.3V and GND pins for all io pins
- Small enough to drop into a PLASTIC North American electrical box
- Actual mounting holes!
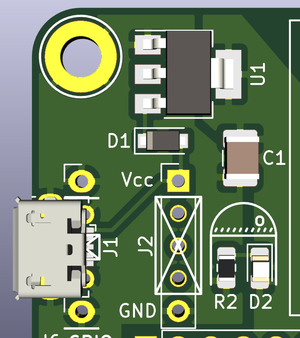
The Building Blocks
Power
- Input:
- Directly soldered USB-micro connector (J1)
- My favourite USB breakout board (J2)
- Direct wiring (J2)
- Reverse polarity protection (D1)
- Regulation (U1 & C1)
- Indication (R2D2) :P
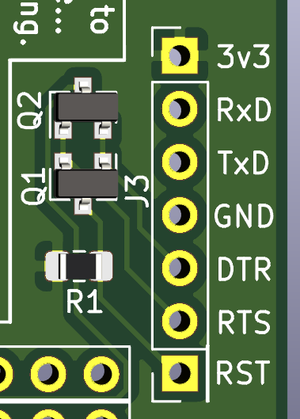
Programming
- Header (J3)
- Pins 1-4 are an exact match for the most common layout used on Sonoff devices.
- Pins 5 & 6 are used (with an appropriate USB-Serial adapter to enable the automatic mode selection
- RST is actually atest point & should be just another pin on J3. But, I didn't originally plan to put it directly inline with J3... so...
- Automatic mode selection (Q1 & Q2)
- This idea was shamelessly stolen from the D1-mini
I/O
- GPIO breakout (J6)
- The ESP8266 (& ESP8285) have 17 GPIO & 1 ADC available. Therefore, I've placed an 18 pin header for I/O on the board.
- Power for sensors etc. (J5)
- Obvious once you look at the board... 18 pins...
- Ground for sensors etc. (J4)
- Obvious once you look at the board... 18 pins...
You will notice that ALL of the boards have the full set of I/O pins. On some (most) of the boards, you'll see (at least on the board views & renders) that some of the GPIO, 3v3 & GND sets are crossed out. The GPIOs are not all broken out on all modules. But, I've left the pin positions in to keep all the boards compatible with each other.
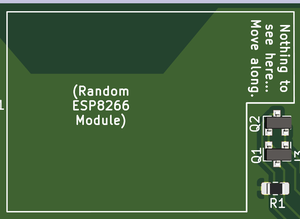
The Module Carrier
- All the empty space on the board... :P
The Resulting Set of Boards
- ESP-M3 Everything!
- (The original board)
- Hardware Has Arrived!!!
- (Gotta build & test yet...)
- ESP-01 Everything!
- ESP-07 Everything!
- ESP-?? Everything!
- (The generic board)
- ESP-SoC Everything!
- (The over board)